Truffle
Overview¶
Truffle is a blockchain development environment, which you can use to create and test smart contracts by leveraging the Ethereum Virtual Machine. This guide aims at teaching how to create a smart contract using Truffle and deploying it on the EVM-compatible Polygon Network.
Note
This tutorial is an adapted version of the Truffle quickstart guide article.
What you will do¶
- Install and set up Truffle.
- Deploy a contract on the Polygon Network.
- Check the deployment status on Polygonscan.
Prerequisites¶
There are a few technical requirements before we start. Please install the following:
- Node.js v8+ LTS and npm (packaged with Node)
- Git
Once we have those installed, we only need one command to install Truffle:
npm install -g truffle
To verify that Truffle is installed properly, type truffle version on a terminal. If you see an error, make sure that the npm modules are added to your path.
Creating a project¶
MetaCoin project¶
We will use one of Truffle’s boilerplates which you can find on their Truffle Boxes page. MetaCoin box creates a token that can be transferred between accounts.
-
Start by creating a new directory for this Truffle project:
mkdir MetaCoin cd MetaCoin -
Download the MetaCoin box:
truffle unbox metacoin
With that last step, you have created a Truffle project containing folders with contracts, deployment, testing, and configuration files.
This is the smart contract data from the metacoin.sol file:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
// Tells the Solidity compiler to compile only from v0.8.13 to v0.9.0
pragma solidity ^0.8.13;
import "./ConvertLib.sol";
// This is just a simple example of a coin-like contract.
// It is not ERC20 compatible and cannot be expected to talk to other
// coin/token contracts.
contract MetaCoin {
mapping (address => uint) balances;
event Transfer(address indexed _from, address indexed _to, uint256 _value);
constructor() {
balances[tx.origin] = 10000;
}
function sendCoin(address receiver, uint amount) public returns(bool sufficient) {
if (balances[msg.sender] < amount) return false;
balances[msg.sender] -= amount;
balances[receiver] += amount;
emit Transfer(msg.sender, receiver, amount);
return true;
}
function getBalanceInEth(address addr) public view returns(uint){
return ConvertLib.convert(getBalance(addr),2);
}
function getBalance(address addr) public view returns(uint) {
return balances[addr];
}
}
Note
Notice that ConvertLib is being imported just after the pragma statement. In this project, there are actually two smart contracts that will be deployed at the end: one is Metacoin, containing all the send and balance logic; the other is ConvertLib, a library used to convert values.
Testing the contract¶
You can run Solidity and Javascript tests.
-
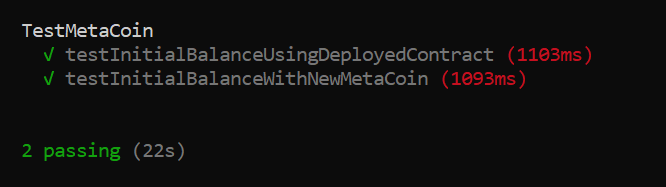
In a terminal, run the Solidity test:
truffle test ./test/TestMetaCoin.solYou should see the following output:
-
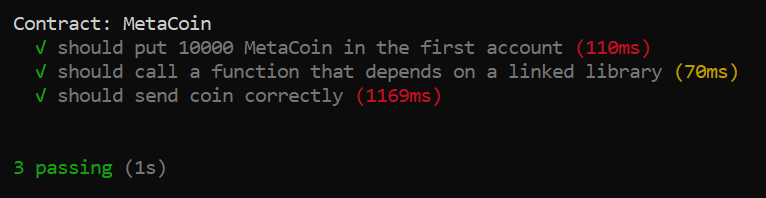
Run the JavaScript test:
truffle test ./test/metacoin.jsYou should see the following output:
Compiling the contract¶
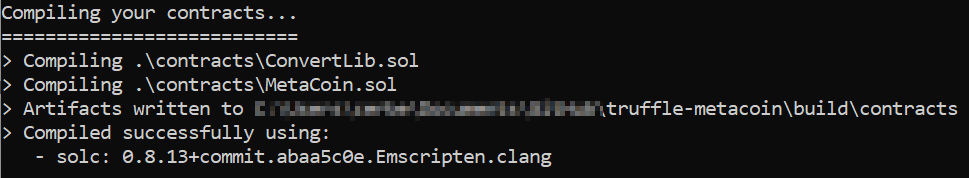
Compile the smart contract using the following command:
truffle compile
You will see the following output:
Configuring the smart contract¶
Before actually depolying the contract, you need to set up the truffle-config.js file, inserting network and compilers data.
Go to truffle-config.js and update the file with Polygon Mumbai network details.
const HDWalletProvider = require('@truffle/hdwallet-provider');
const fs = require('fs');
const mnemonic = fs.readFileSync(".secret").toString().trim();
module.exports = {
networks: {
development: {
host: "127.0.0.1", // Localhost (default: none)
port: 8545, // Standard Ethereum port (default: none)
network_id: "*", // Any network (default: none)
},
matic: {
provider: () => new HDWalletProvider(mnemonic, `https://rpc-mumbai.maticvigil.com`),
network_id: 80001,
confirmations: 2,
timeoutBlocks: 200,
skipDryRun: true
},
},
// Set default mocha options here, use special reporters etc.
mocha: {
// timeout: 100000
},
// Configure your compilers
compilers: {
solc: {
version: "0.8.13",
}
}
}
Note that it requires mnemonic to be passed in for maticProvider. This is the seed phrase (or private key) for the account you would like to deploy from. Create a new .secret file in the root directory and enter your 12-word mnemonic seed phrase to get started. To get the seed words from MetaMask wallet, you can go to MetaMask settings, then from the menu, choose Security and Privacy where you will see a button that says reveal seed words.
Deploying on Polygon network¶
Add MATIC to your wallet using Polygon Faucet. Next, run this command in the root folder of the project directory:
truffle compile
truffle deploy --network matic
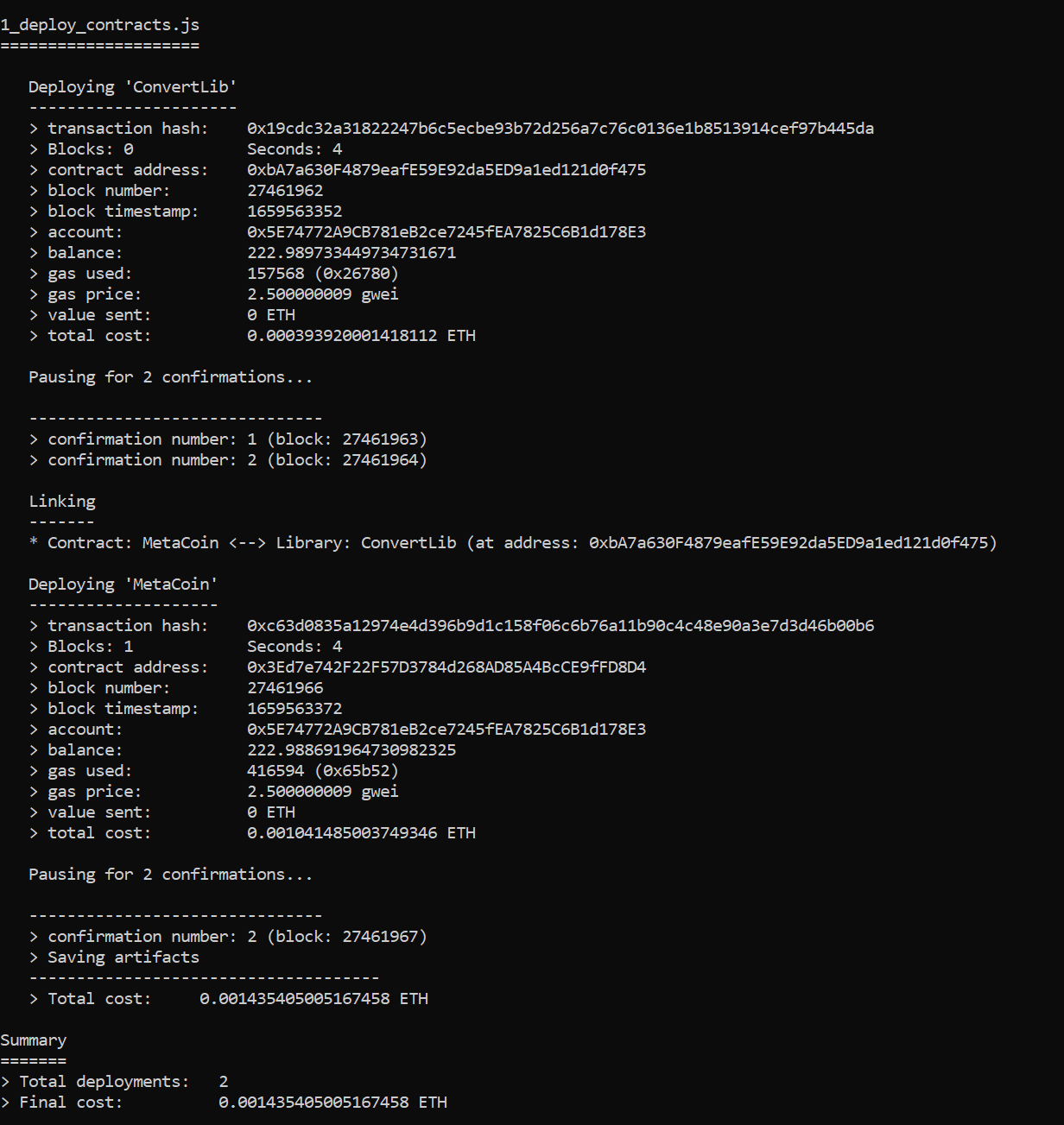
Note
Remember your address, transaction_hash and other details provided would differ. Above is just to provide an idea of the structure.
Congratulations! You have successfully deployed a smart contract using Truffle. Now you can interact with the contract and also check its deployment status on Polygonscan.